11th August 2023
Introduction
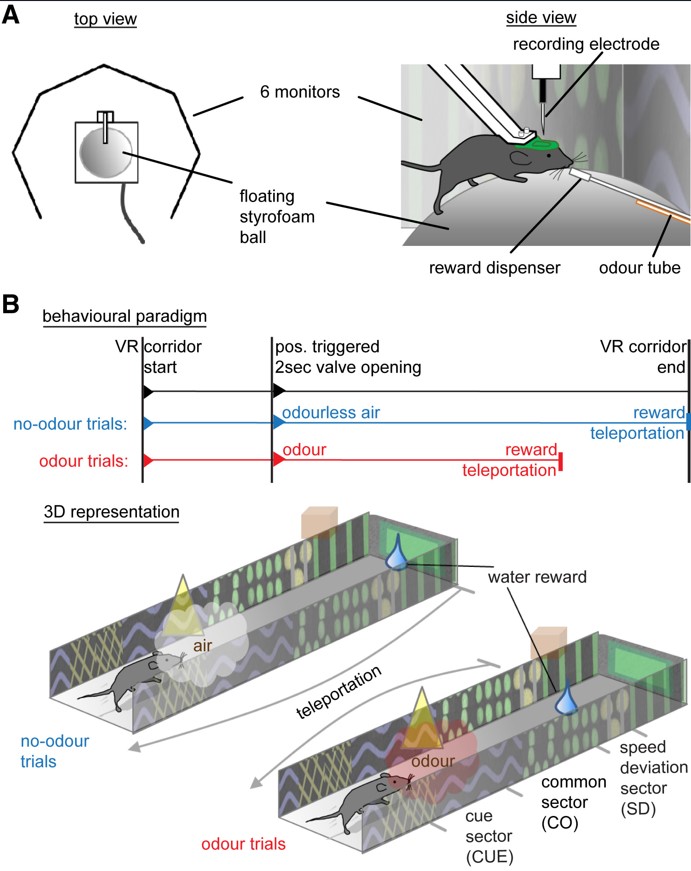
Our brain is like a fascinating puzzle, and the hippocampus holds a special piece that helps us find our way and remember important moments. But there’s still a lot we don’t know about a specific group of brain cells called GABAergic interneurons and how they contribute to these processes. To uncover their role, Thomas Forro and Thomas Klausberger from the Medical University of Vienna took mice on a virtual reality adventure, using the PhenoSys JetBall system in combination with the Olfactometer. What they discovered not only sheds light on spatial memory but also reveals the unique contributions of these interneurons.
Mapping Memories in a Virtual World
Imagine mice exploring a virtual maze, associating different smells with specific spots. Surprisingly, when a certain smell predicted a different reward location, the activity of specific cells in the hippocampus rearranged, as if creating a mental map. To understand this phenomenon, Forro and Klausberger closely monitored specific interneurons in head-fixed mice during navigation in the odor-augmented virtual maze. They focused on a type called parvalbumin (PV)-expressing basket cells and found that their activity changed in sync with the maze’s working memory sections.
Unveiling the Differences
These interneurons showed intriguing behaviors. While the PV-expressing basket cells responded to contextual changes in the working-memory-related sections of the maze, another type called PV-expressing bistratified cells did not. Additionally, some interneurons, including those expressing cholecystokinin, had reduced activity during spatial navigation but increased activity during rewarding moments.
Implications for How Our Brain Works
These findings suggest that different types of GABAergic interneurons play specific roles in how our hippocampus processes information. They contribute to creating mental maps and shaping spatial memory. This newfound understanding opens doors for further research into the intricate workings of these interneurons and their impact on our cognitive abilities.