ColonyRack
Automated Tracking of Individual Animals in Large groups in a semi-natural environments
The ColonyRack is an innovative, RFID-based system for automating the monitoring and tracking of large groups of mice, providing continuous, individual behavioral data within a complex, multi-cage housing environment.
The PhenoSys ColonyRack system revolutionizes large rodent colony studies by integrating advanced RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) technology into a multi-cage rack setup. Designed for efficiency and precision, it automatically tracks and identifies individual animals within their group-housed environments, providing continuous, 24/7 data on activity, location, and interactions.. It opens-up new dimension of studying mice in large groups with unbiased data collection, without operator intervention .
The ColonyRack transforms standard housing into a sophisticated behavioral phenotyping platform and allows researchers to gain comprehensive, long-term insights into individual and social behaviors across large cohorts.
The ColonyRack was developed in close cooperation with the group of Prof. Dr. Gerd Kempermann at the DZNE, Dresden.
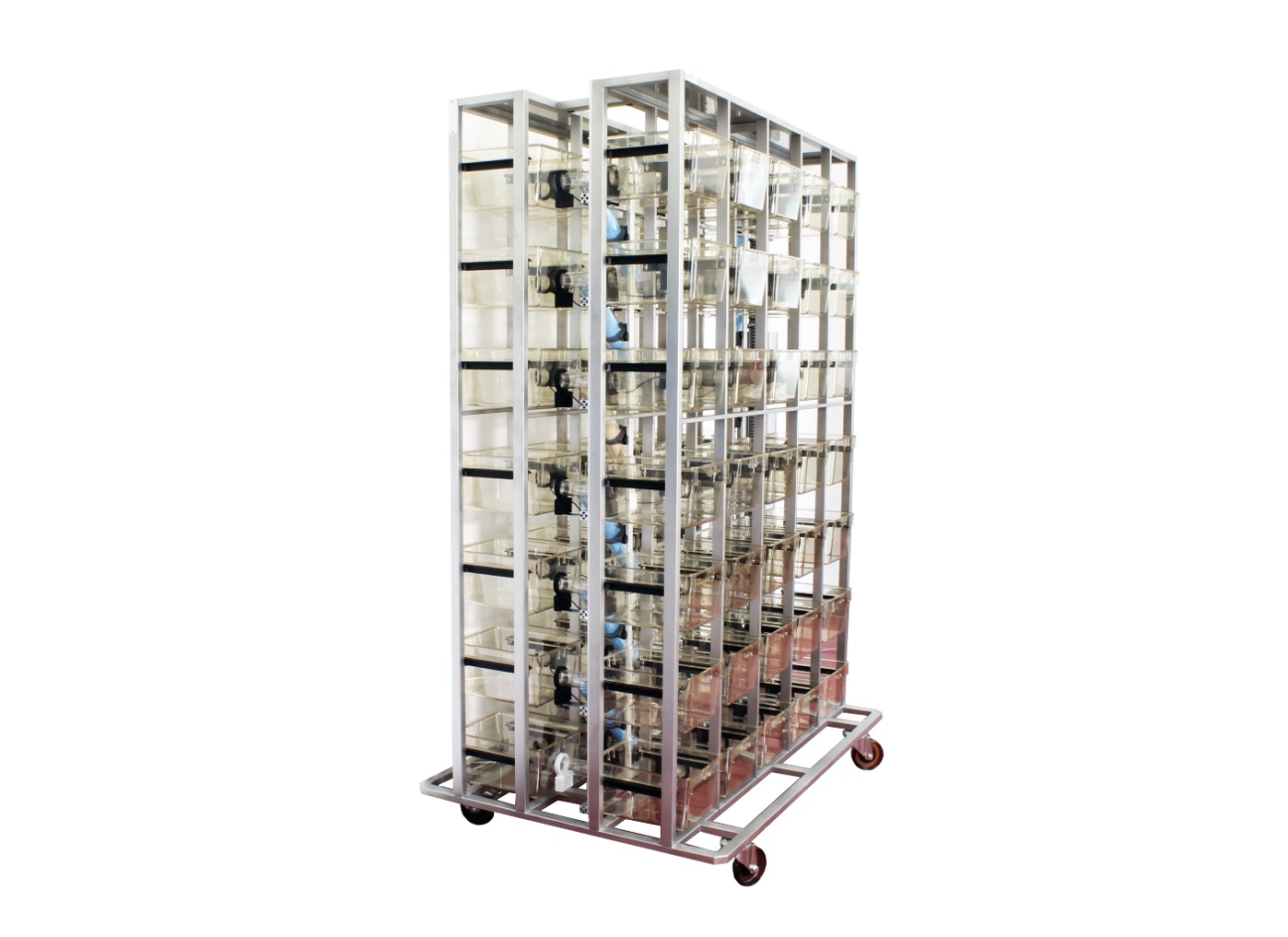

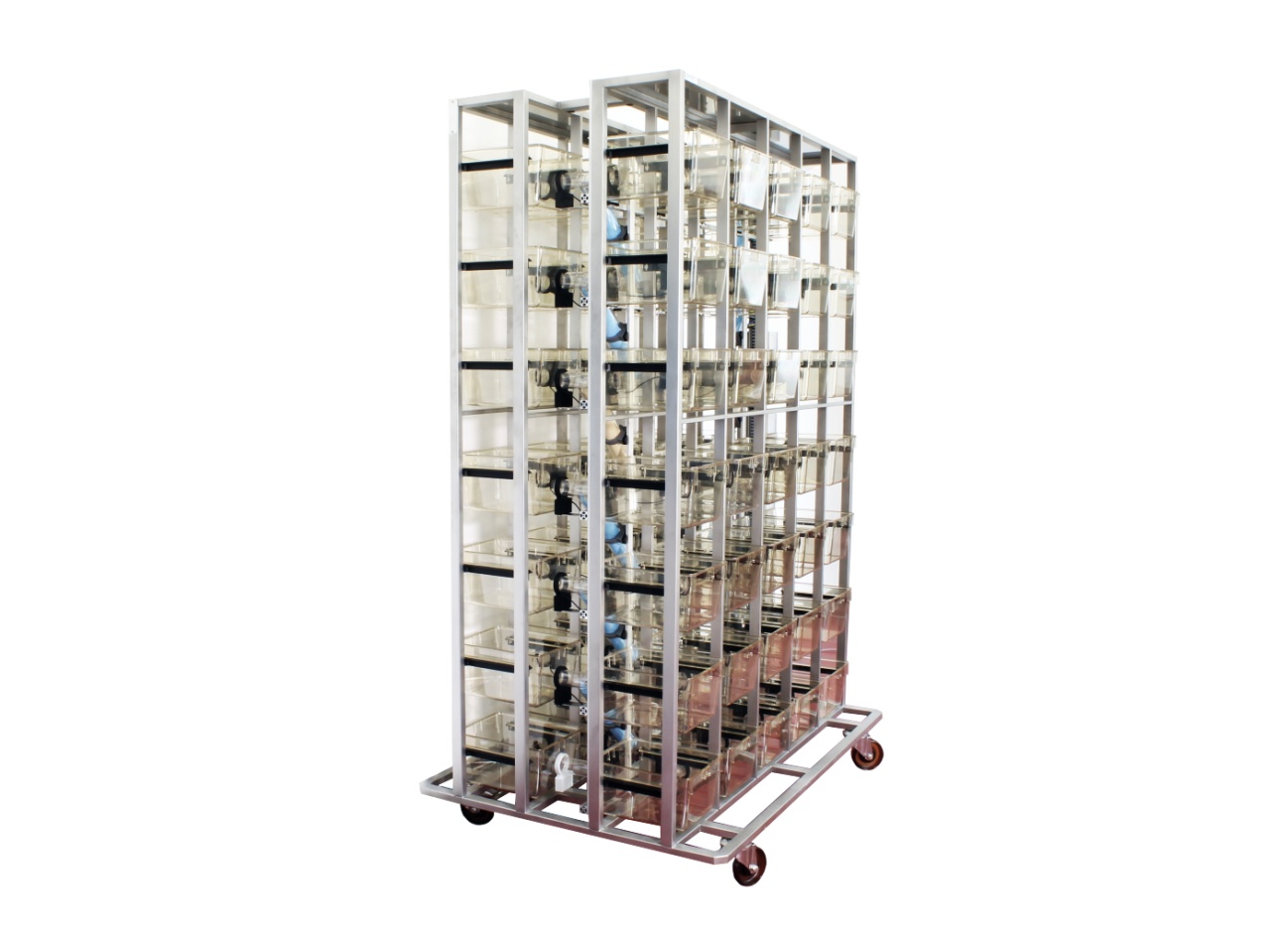
Features
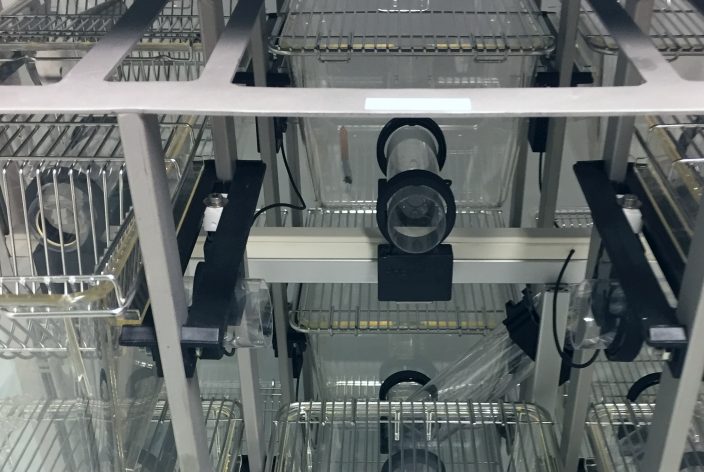
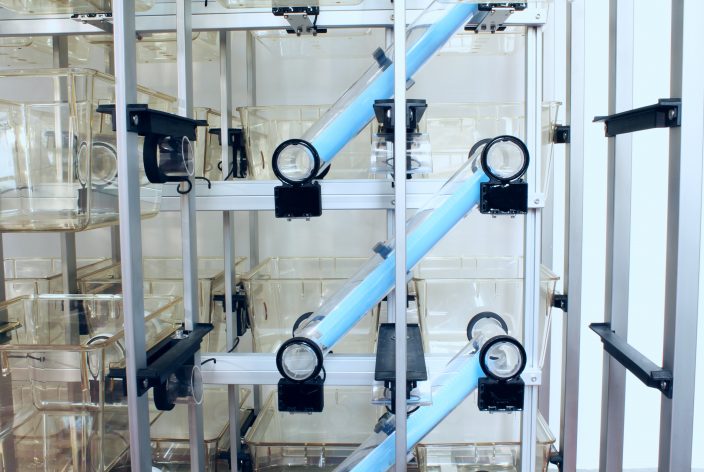
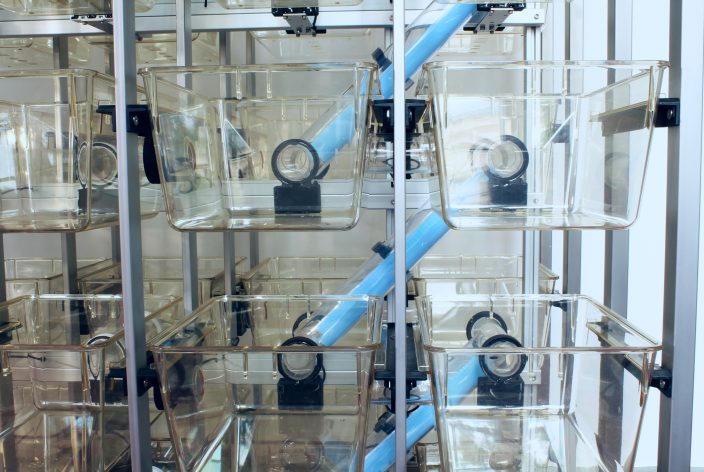
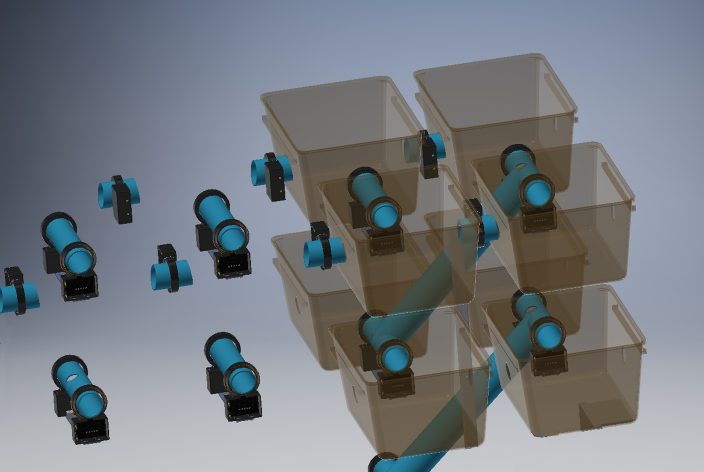
8, 18, or 70 cages in standardized rack mounts
Interconnecting tubes between all cages and levels
RFID readers at each connection
Micro-controllers and PC for data acquisition´.
Software with 24/7 data acquisition
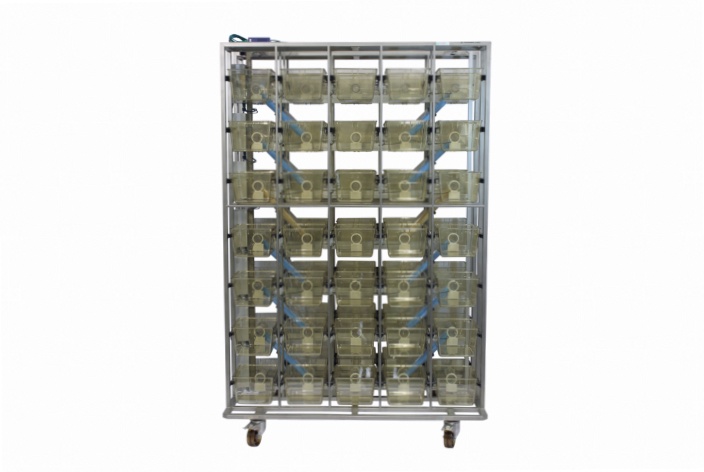
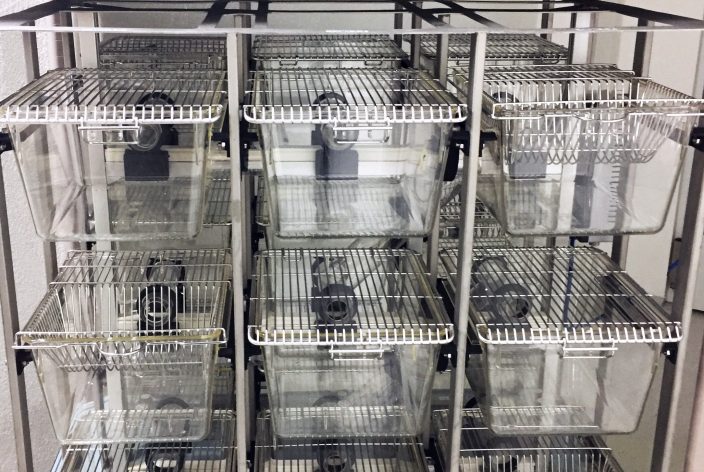







Key Benefits
Automated Individual Tracking Across Cages
![]() RFID Technology: Reliably identifies and tracks each mouse in real-time as they move between interconnected cages in the rack.
RFID Technology: Reliably identifies and tracks each mouse in real-time as they move between interconnected cages in the rack.
![]() Seamless Data Collection: Provides continuous data on activity, sociability and explorative behaviour for each animal.
Seamless Data Collection: Provides continuous data on activity, sociability and explorative behaviour for each animal.
Scalable for Large Cohorts
![]() Multi-Cage Rack System: Designed to accommodate numerous cages within a single rack, enabling large-scale, high-throughput studies.
Multi-Cage Rack System: Designed to accommodate numerous cages within a single rack, enabling large-scale, high-throughput studies.
![]() Efficient Colony Management: Automates tracking, reducing labor and the need for frequent human intervention.
Efficient Colony Management: Automates tracking, reducing labor and the need for frequent human intervention.
24/7 Continuous Monitoring
![]() Uninterrupted Data Capture: Records behavioural data around the clock, providing comprehensive insights into activity patterns, and social interactions over long periods.
Uninterrupted Data Capture: Records behavioural data around the clock, providing comprehensive insights into activity patterns, and social interactions over long periods.
 Reduced Stress: Minimizes disturbances to animals, fostering more natural and ecologically valid behaviors.
Reduced Stress: Minimizes disturbances to animals, fostering more natural and ecologically valid behaviors.
Flexible Cage Connectivity
![]() Interconnected Cages: Allows animals to move freely between cages, promoting complex social interactions and environmental exploration.
Interconnected Cages: Allows animals to move freely between cages, promoting complex social interactions and environmental exploration.
![]() Modular Design: Adaptable to various cage types and overall size of the habitat.
Modular Design: Adaptable to various cage types and overall size of the habitat.
Integrated Data Management & Analysis
 Reliable Detection: Ensures consistent and accurate detection of RFID-tagged animals.
Reliable Detection: Ensures consistent and accurate detection of RFID-tagged animals.
![]() Software Integration: Works with accompanying software- PhenoSoft Control, to log all detection events for later analysis.
Software Integration: Works with accompanying software- PhenoSoft Control, to log all detection events for later analysis.
Applications

Studying Individuality
Picks-up even small variance of specific behaviors in a group of genetically identical animals

High-Throughput Phenotyping
Efficiently characterize behavioral and activity patterns across large cohorts of genetically modified animals.

Drug Screening & Efficacy Studies
Evaluate the long-term effects of pharmacological compounds on individual and social behavior.

Social Behavior & Interaction Studies
Gain unprecedented data on individual animal's movement and presence within complex social groups.
Publications
Featured in numerous peer-reviewed studies across leading neuroscience journals.
Ehret F, Pelz MS, Senko AN, Soto KEG, Liu H, Kempermann G. Presymptomatic Reduction of Individuality in the AppNL-F Knockin Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Biol Psychiatry. 2023 Nov 1.
Journal : Biological Psychiatry, 94(9), 721-731, 2023
DIO : 10.1016/j.biopsych.2023.04.009
G. Kempermann et al., (2022). The individuality paradigm: Automated longitudinal activity tracking of large cohorts of genetically identical mice in an enriched environment. Neurobiology of Disease.
Journal : Neurobiology of Disease, 172, 105820, 2022
DIO : 10.1016/j.nbd.2022.105820
S. Zocher et al., (2020). Early-life environmental enrichment generates persistent individualized behavior in mice. Science Advances.
Journal : Science Advances, 6(39), eabb1478, 2020
DIO : 10.1126/sciadv.abb1478
Have Questions?
Contact Us
Get in touch with us and let us know how we can assist you.